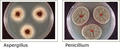
Aspergillus/Penicillium-Like
This category is included on laboratory analysis reports for air samples containing certain free spores without other identifying structures. The free spores of Aspergillus and Penicillium (and other genera with small, round or ovoid, and colorless spores) are essentially indistinguishable, using standard microscopic examination methods. If required, cultured specimens can provide additional characteristics that will enable technicians to determine what genus is represented. If sporulating structures are present, Aspergillus is readily identifiable on tape samples. [Discovery of the Aspergillus species requires the culture of the fungus under different conditions of media, humidity, and temperature. Identifying Penicillium species is difficult, but, in some cases, possible. These two allergenic molds are among those most often found in contaminated buildings. Aspergillus is represented by numerous species, many of which produce toxic substances. It may be associated with symptoms such as sinusitis, allergic bronchiopulmonary aspergillosis, and other allergic symptoms. As if not to be outdone, Penicillium too is found in increased numbers in interiors. Some of its many species produce toxic substances that can cause allergic reactions, mucous membrane irritation, headaches, vomiting, and diarrhea.